Fighting poverty
Successful debt relief

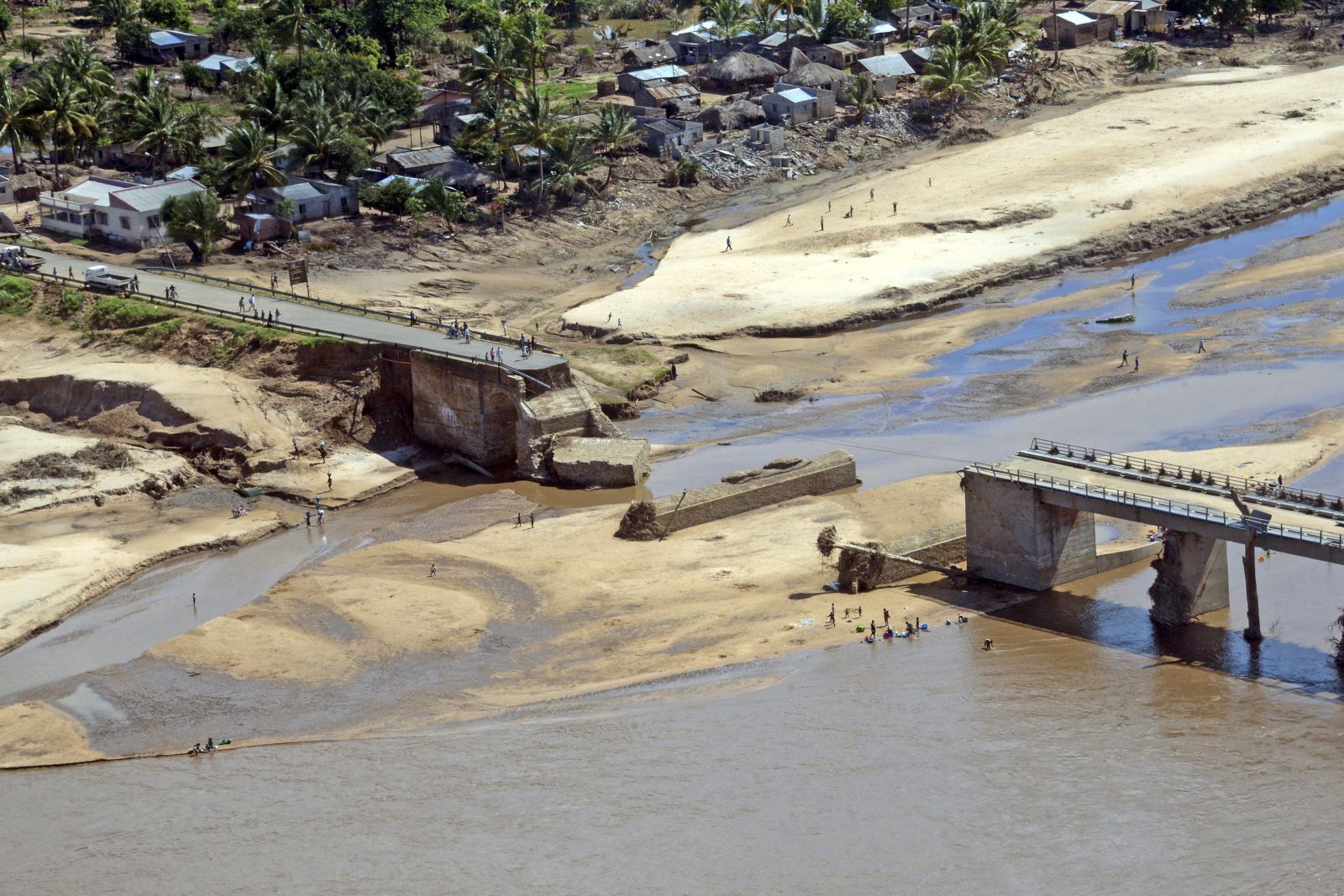
Thirty-six countries, of which 30 are African, benefited from the HIPC initiative. Their debt situation improved substantially. They also made solid progress in economic and social terms. About 75 % of the economies concerned grew continuously for at least 10 years. Some diversified, with new industries emerging. That happened in Rwanda, Ghana, Ethiopia and Senegal for example. Statistics on health and educational performance improved fast.
The way the initiative was designed made the difference. The countries concerned had to draft “poverty reduction strategy papers” (PRSPs). The term itself proves they were not just about improving short-term competitiveness on world markets. The focus was now on issues that earlier structural-adjustment programmes had largely ignored.
PRSP implementation was monitored regularly. IMF, World Bank and other international donors made further support dependent on PRSP performance. A particular incentive for governments was that considerable debt-relief would be the reward for full implementation. It turned out, moreover, that the PRSPs were a good basis for ongoing debate between donors and recipient governments, ensuring that donor support was aligned to national exigencies. Another strong point was the long-term outlook. The development of institutional capacities was a core objective. (jz)
Correction 2.11.2018: HIPC stands for “heavily-indebted poor countries” rather than “highly-indebted poor countries”, as was stated in a previous version. The mistake was made in the editing process. We apologise to readers and the author.