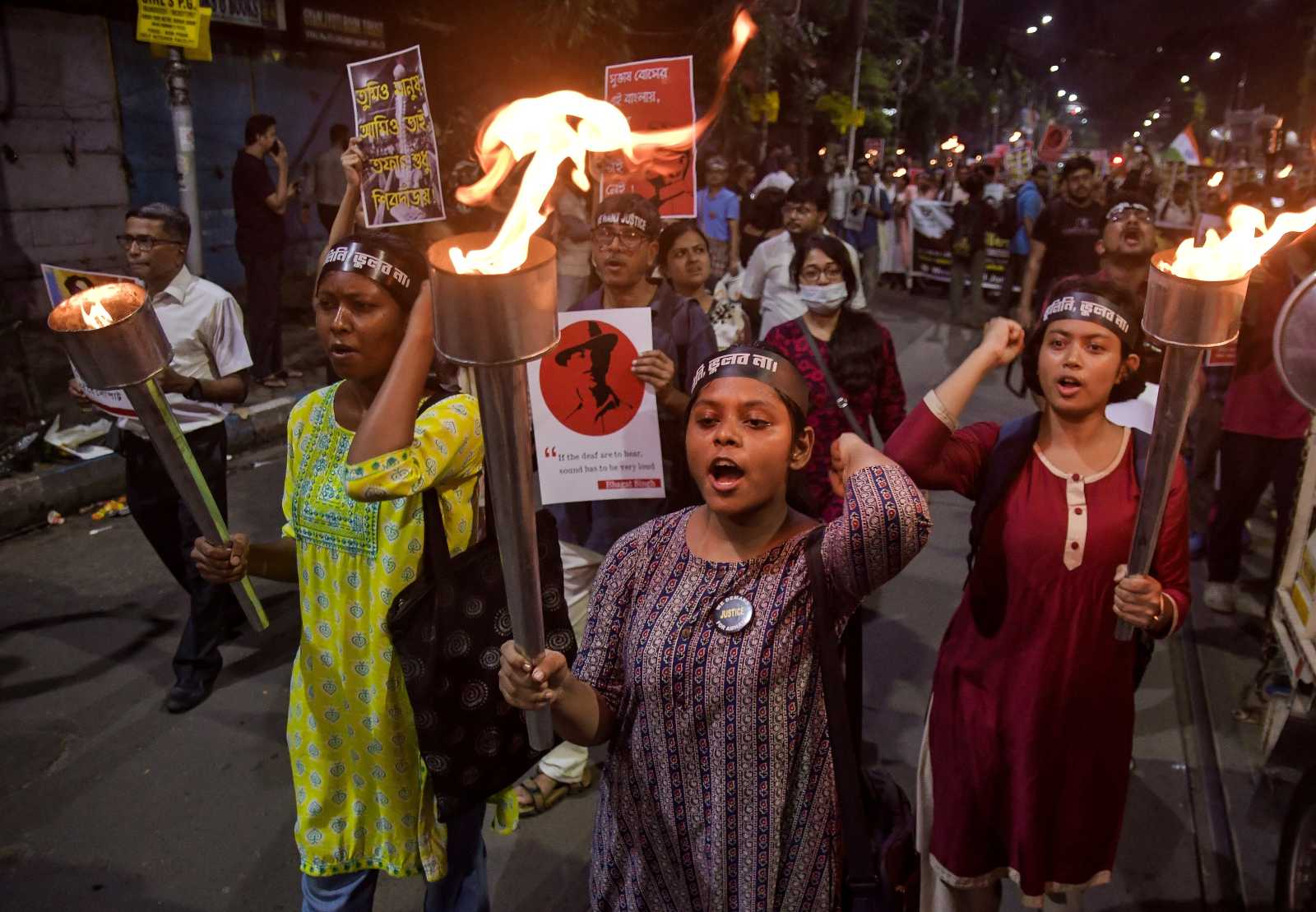Gender equality
Empowering women and girls is crucial to achieving gender justice.

Enforcing women’s rights
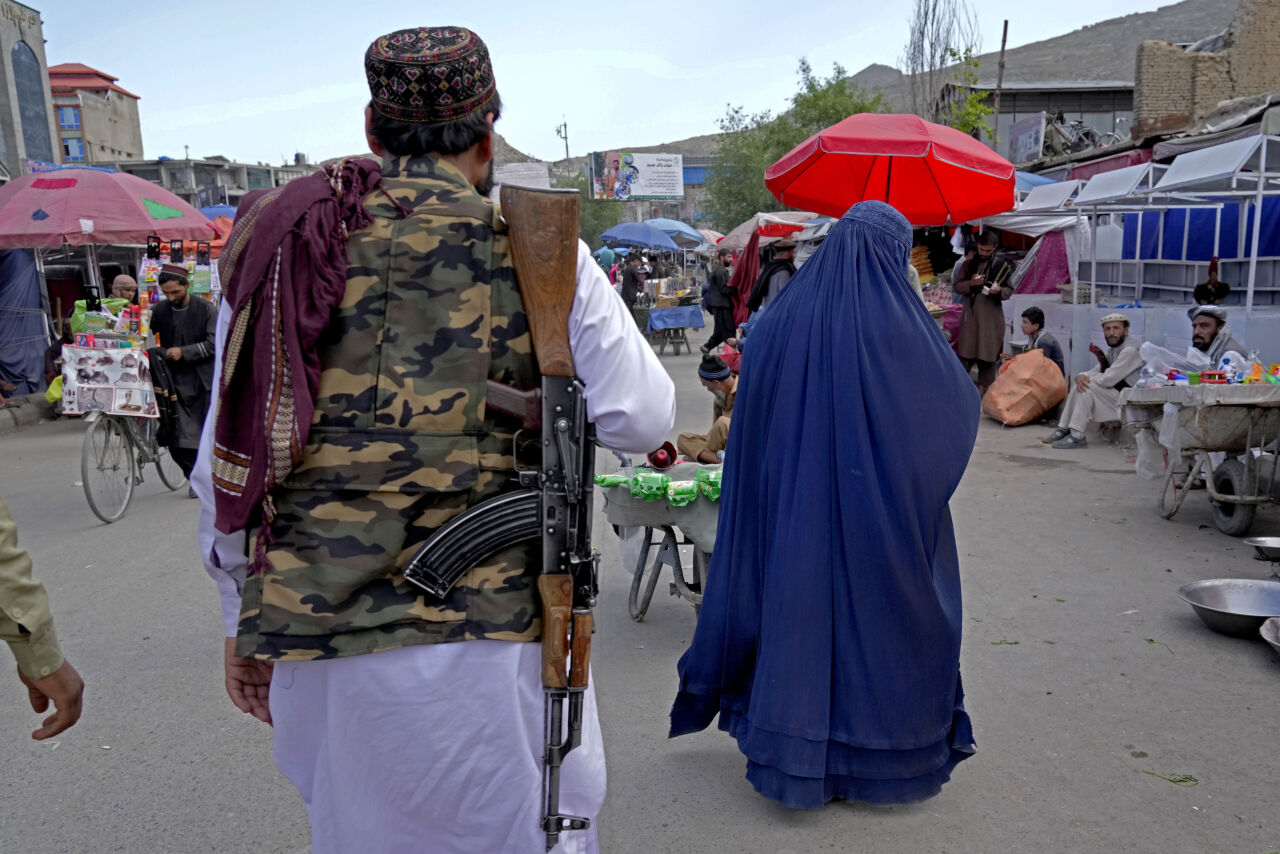
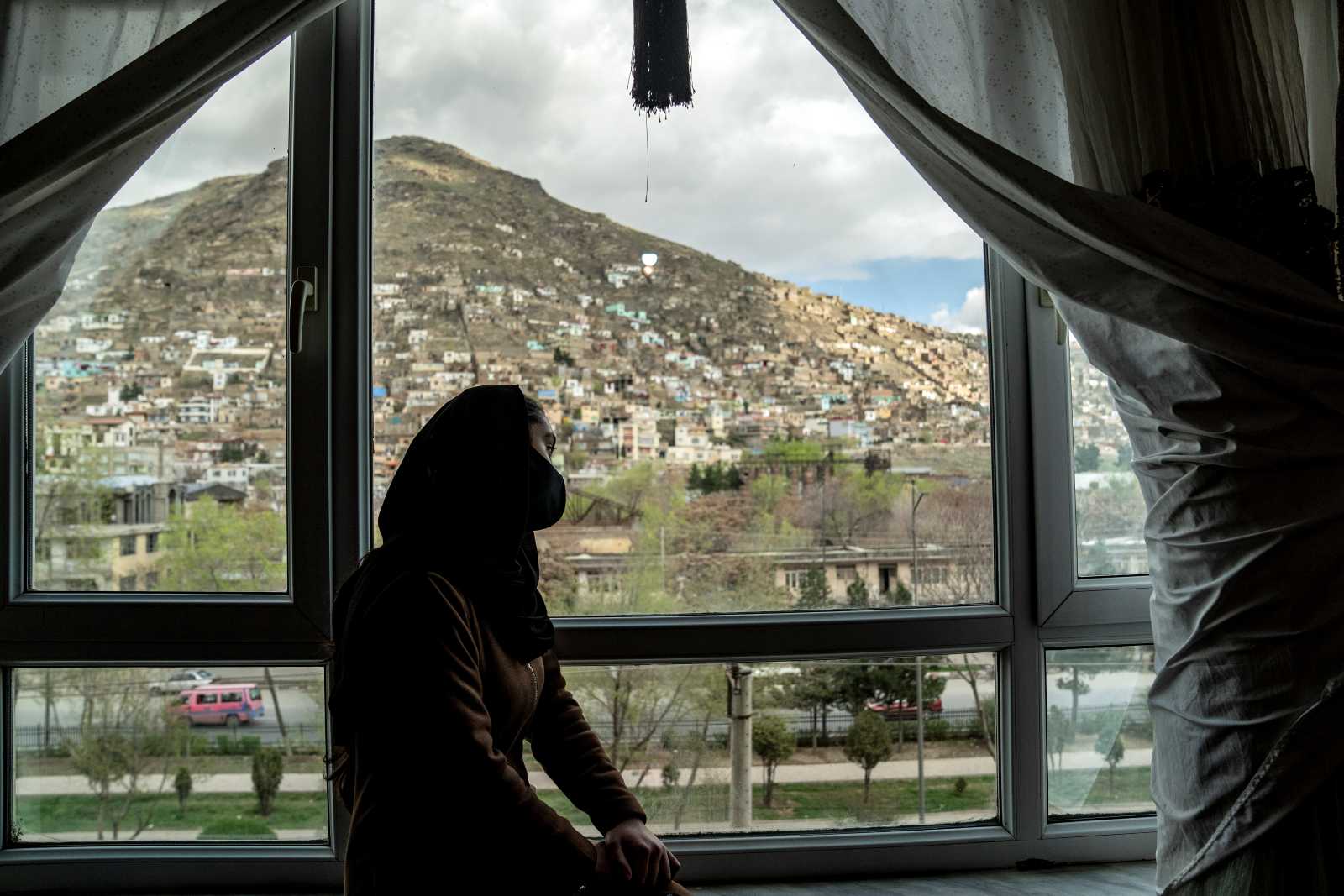
In many countries worldwide, women are facing discriminating laws. They have fewer opportunities to develop and receive less pay for the same work. All over the world, women are asserting themselves, but change is slow. There are setbacks as well, for example in Afghanistan, where the misogynist Taliban have taken over the regime.
Ending all forms of discrimination against women and girls by 2030 is the fifth UN Sustainable Development Goal (SDG). According to the United Nations, gender equality is not only a fundamental human right, but necessary for peace, economic development and sustainability on an international level. Not only should women and girls be equal to men before the law, but gender equality should also permeate everyday life. Where this is not the case, negative impacts on society as a whole emerge.
Recent articles
New contributions on gender justice
Gender equality is one of the core topics of D+C/E+Z. Our authors regularly report on the role of girls and women worldwide. Here you can find current articles related to the topic.
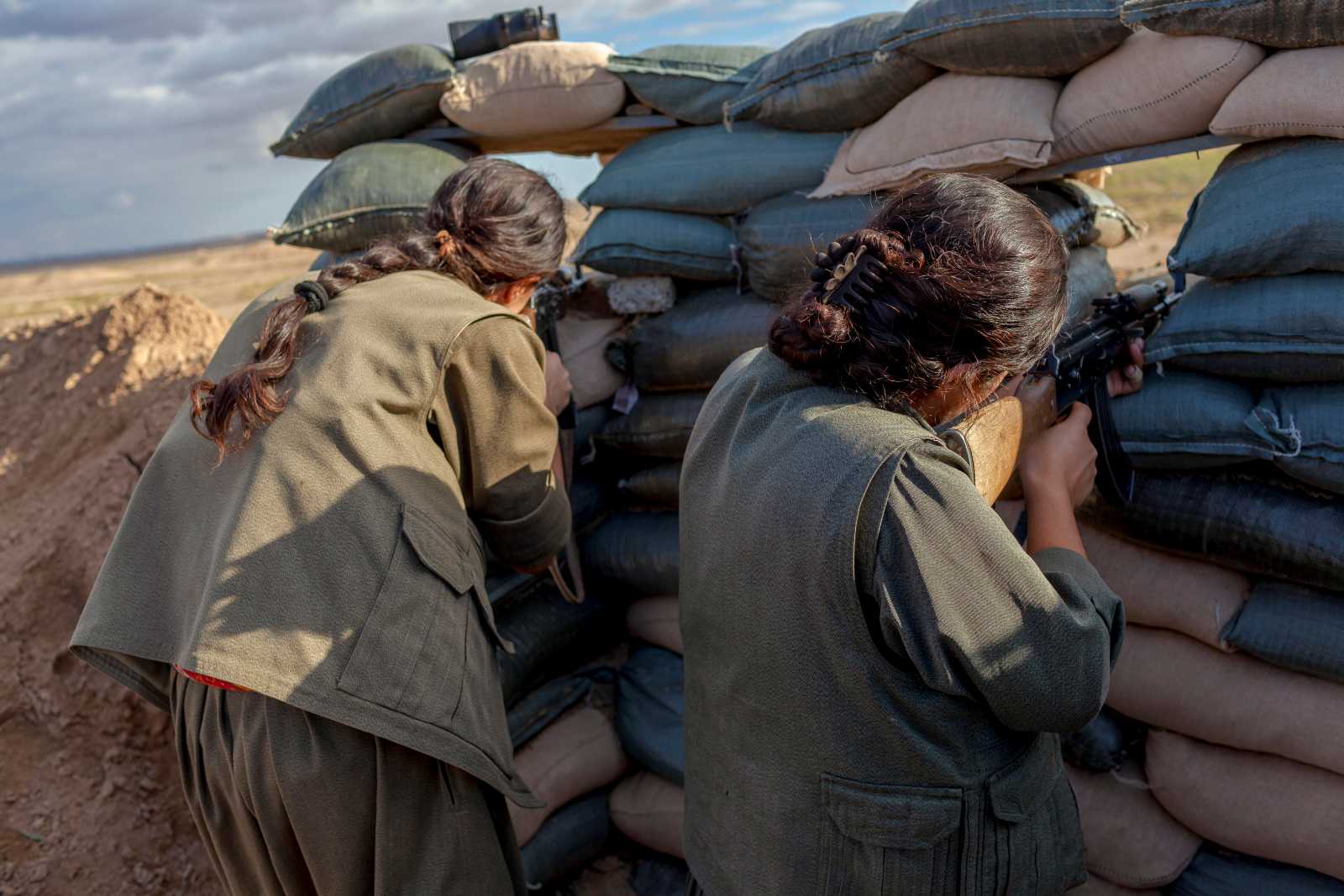
Patriarchal societies
Social oppression
Deep-rooted patriarchal traditions stand in the way of gender equality. Most power is still in the hands of men. They hold positions of influence - there is no real gender equality in political parliaments as well as in big corporations and organisations. The proportion of women in positions of power is growing, at least in parts of the world. However, barriers in policy and legislation need to be removed to accelerate this process.
Women in work
Economic disadvantages
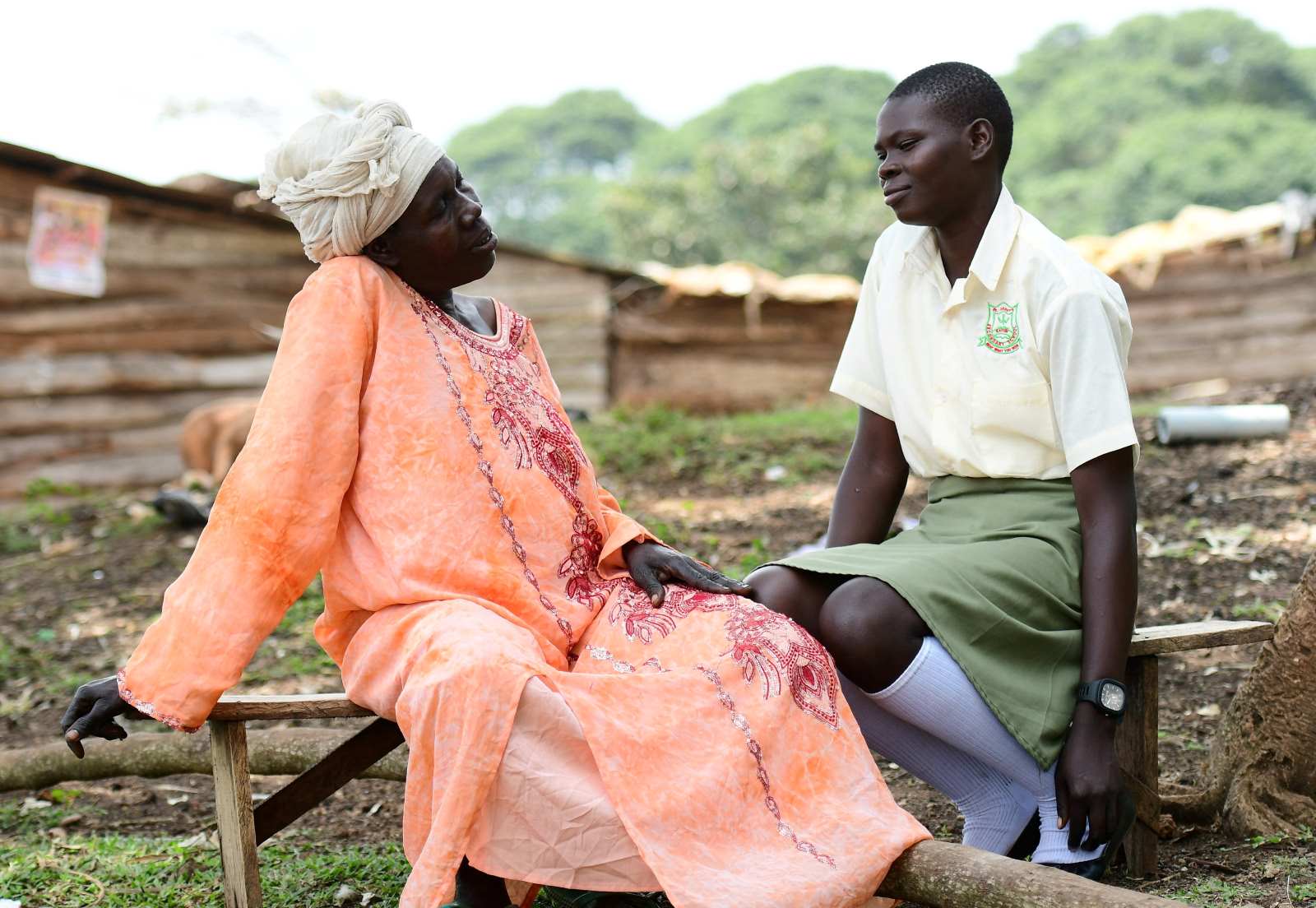
In many countries, women have less access to the labour market than men. If they find a job, they often receive less pay for the same work. In addition, they often do a lot of unpaid work, like taking care of relatives. Women are particularly affected by economic crises, because they tend to lack social security. Gender inequality already starts in school, as girls do not have the same educational opportunities as boys internationally.
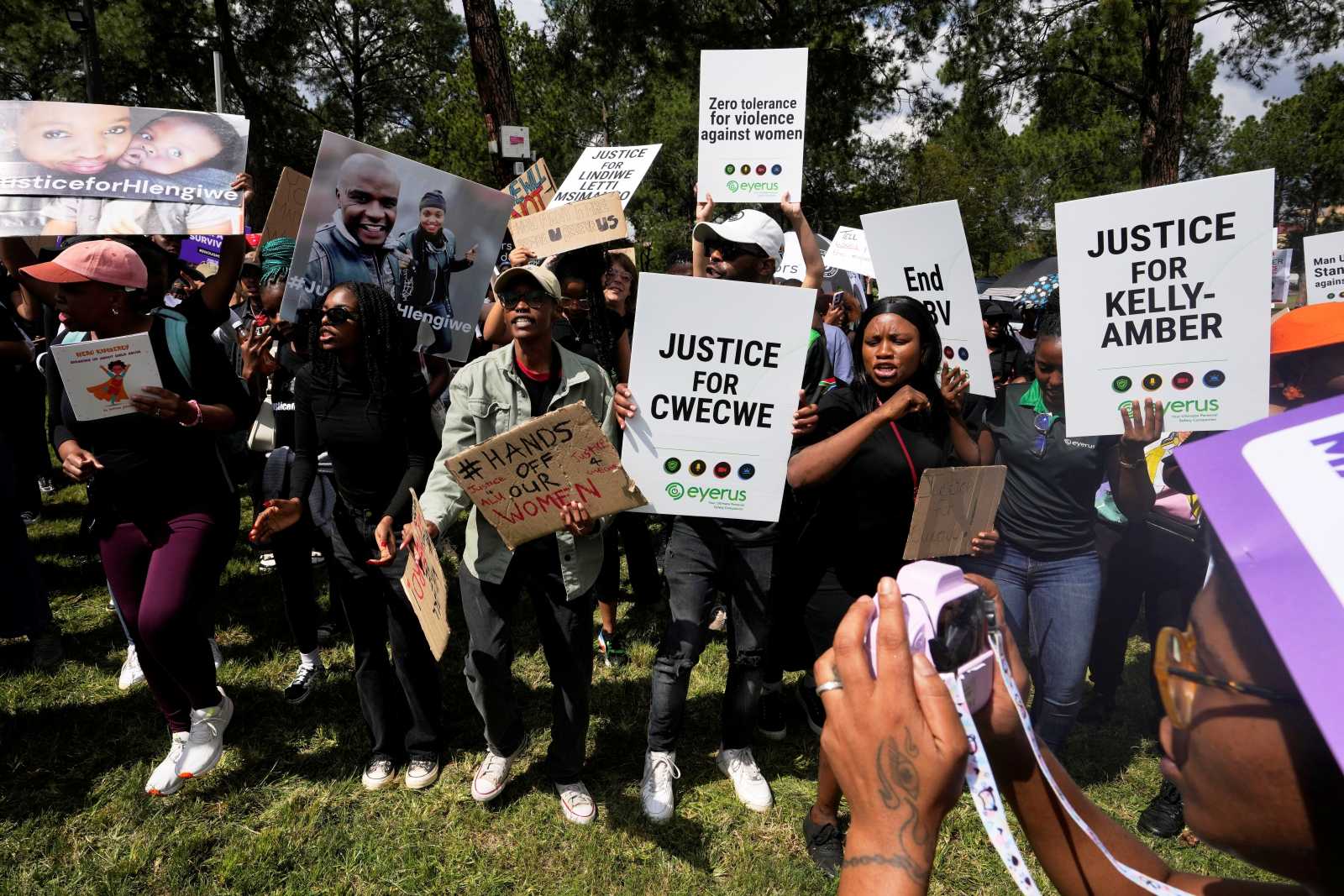
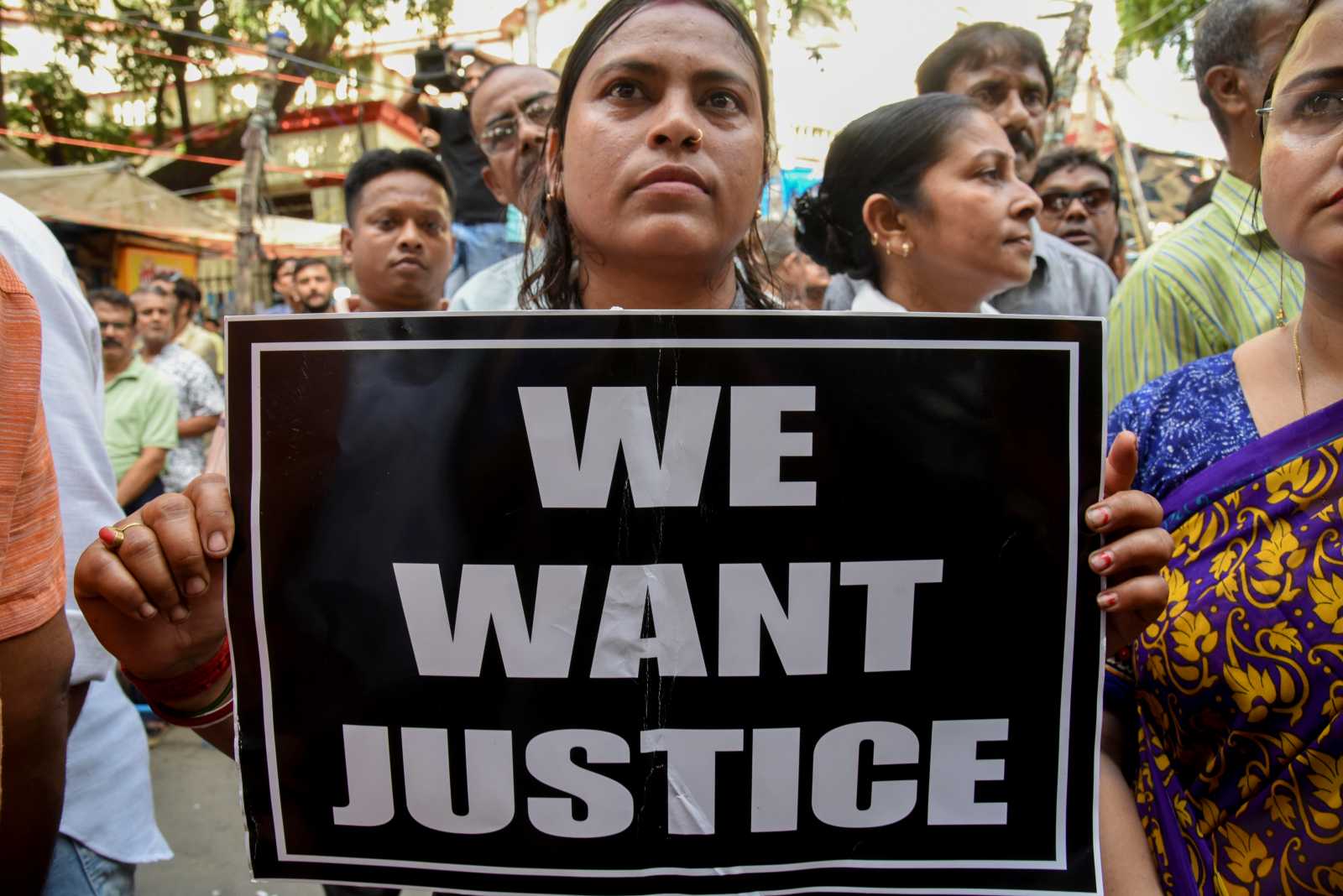
Violence against women
Protect victims, prosecute perpetrators
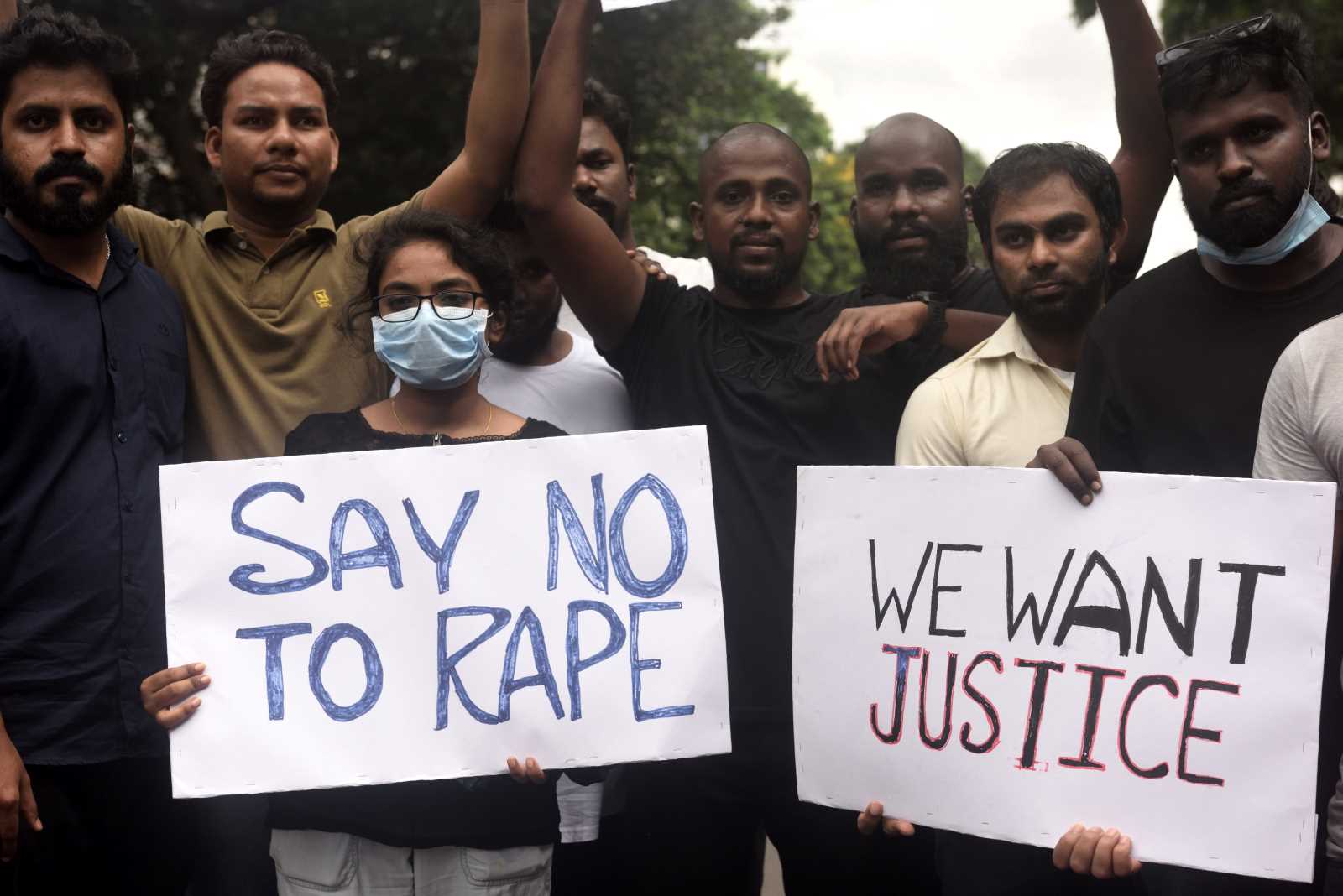
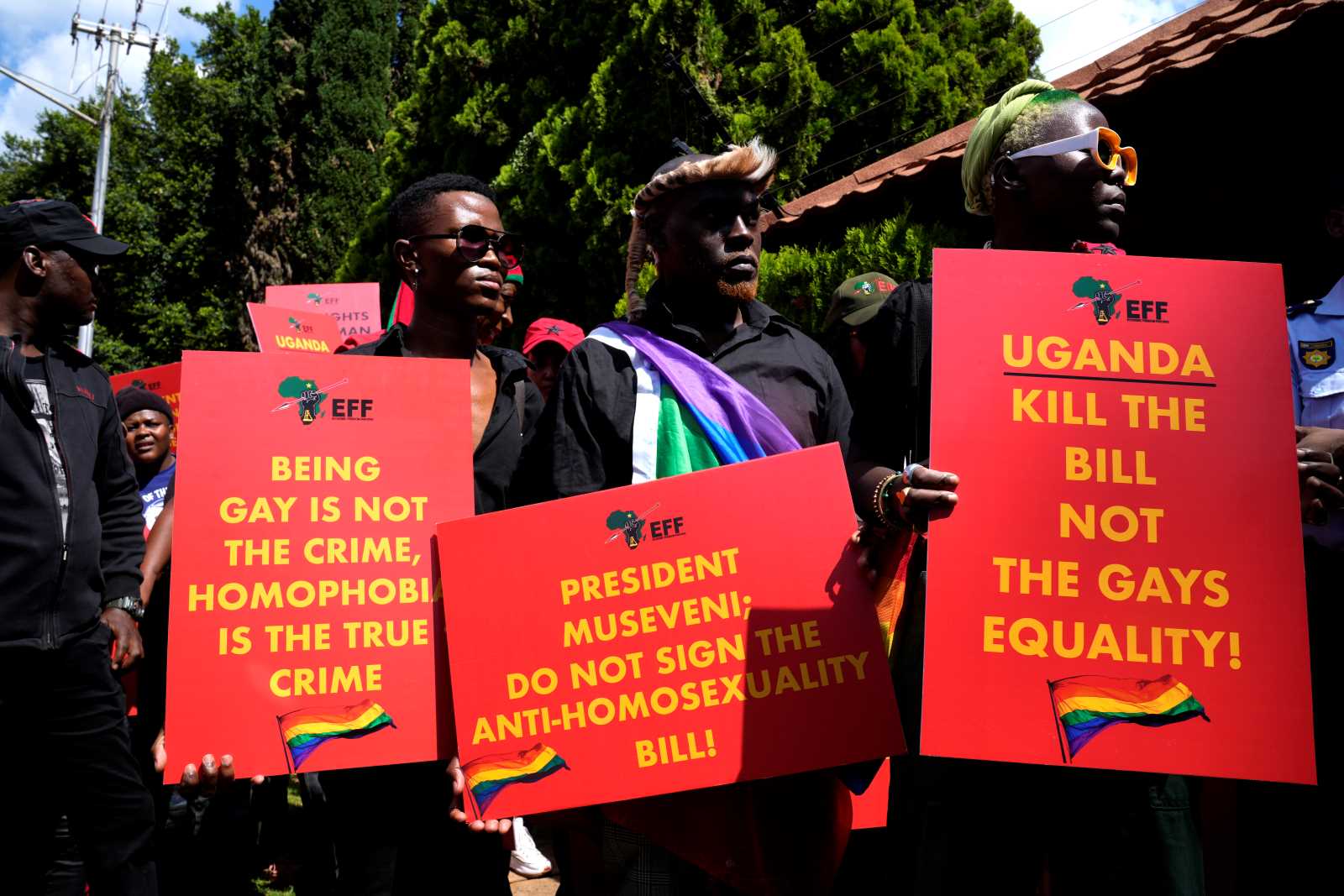
Violence against women takes many forms: from domestic violence to targeted rape in armed conflicts to social pressure in male-dominated societies. Child marriages are also part of it. They deprive girls and young women of the opportunity to shape their lives according to their own ideas. Gender-based violence increased during the Covid-19-pandemic.
Leading a self-determined life
Being in control of one's own body
In many parts of the world, menstruation is stigmatised and girls and women feel ashamed of it. Childlessness is also often considered a stigma. In addition, women often do not have access to maternal health or legal and safe abortion. Especially during conflicts and natural disasters, sexual and reproductive health is often overlooked. All of this prevents women from having control over their own bodies. In some countries, however, significant progress has been made, for example in abortion rights, and relevant programmes have been set up.
Digital Monthly on women's resistance
Digital Monthly on women's resistance
Our Digital Monthly 2025/02 focuses on women's resistance and achievements around the world. Click on the title on the left to download the issue as a PDF free of charge.
The contributions of our authors deal, among other things, with
- the struggle and resistance of women in Afghanistan,
- fighting domestic violence in Uzbekistan,
- support of women from indigenous communities in Mexico,
- the modern African women's movement,
- the role of men in supporting feminism and
- gender-based violence in the workplace in Tanzania.